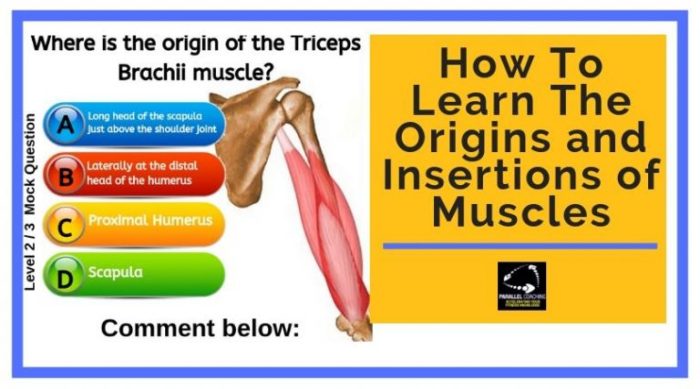
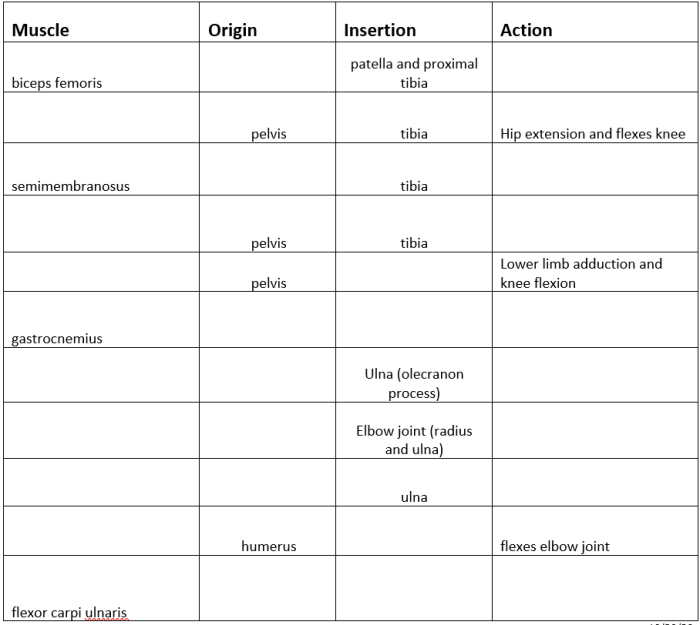
Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of muscle origin and insertion, where the foundations of human movement are laid bare. This muscle origin and insertion quiz will unravel the intricacies of these anatomical landmarks, empowering you with a profound understanding of their functional significance and clinical implications.
Delve into the diverse types of muscle origins and insertions, unraveling their unique characteristics and functional implications. Discover how these attachments orchestrate joint movements, shaping our every action and enabling the symphony of human motion.
Muscle Origin and Insertion Definitions
Muscle Origin: The point of attachment of a muscle to a relatively fixed or immobile bone.
Muscle Insertion: The point of attachment of a muscle to a more movable bone.
Differences between Muscle Origin and Insertion: Origin is generally closer to the trunk or axial skeleton, while insertion is closer to the extremities. The origin is usually the less movable attachment point, while the insertion is the more movable attachment point.
Types of Muscle Origins and Insertions
Types of Muscle Origins:
- Aponeurosis: A sheet of fibrous tissue that connects a muscle to a bone.
- Tendon: A tough, fibrous cord that connects a muscle to a bone.
- Periosteum: The fibrous membrane that covers the outer surface of a bone.
- Cartilage: A specialized connective tissue that covers the ends of bones and provides cushioning.
Types of Muscle Insertions:
- Aponeurosis: A sheet of fibrous tissue that connects a muscle to a bone.
- Tendon: A tough, fibrous cord that connects a muscle to a bone.
- Fascia: A layer of fibrous tissue that surrounds muscles and organs.
- Another muscle: Some muscles insert directly into other muscles.
Examples of Muscles with Specific Origin and Insertion Types:
- Biceps brachii: Originates from the scapula (aponeurosis) and inserts into the radius (tendon).
- Gluteus maximus: Originates from the ilium (aponeurosis) and inserts into the femur (tendon).
- Pectoralis major: Originates from the sternum (cartilage) and inserts into the humerus (tendon).
Functional Implications of Muscle Origin and Insertion, Muscle origin and insertion quiz
Muscle origin and insertion influence muscle function by determining the direction of pull and the range of motion.
Relationship between Muscle Origin and Insertion and Joint Movement:
- Flexors: Muscles that cross the anterior side of a joint and cause flexion.
- Extensors: Muscles that cross the posterior side of a joint and cause extension.
- Abductors: Muscles that move a body part away from the midline.
- Adductors: Muscles that move a body part towards the midline.
Examples of how Muscle Origin and Insertion Affect Movement:
- Biceps brachii: Flexes the elbow joint.
- Gluteus maximus: Extends the hip joint.
- Pectoralis major: Adducts the arm.
Clinical Significance of Muscle Origin and Insertion
Understanding muscle origin and insertion is important in clinical settings because it aids in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders.
Examples of the Clinical Relevance of Muscle Origin and Insertion:
- Muscle tears: Tears can occur at the origin or insertion of a muscle, causing pain and weakness.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of a tendon can occur at the point of insertion.
- Muscle atrophy: Loss of muscle mass can occur due to injury or disuse, affecting muscle origin and insertion.
Assessment and Evaluation of Muscle Origin and Insertion
Muscle origin and insertion can be assessed through various techniques.
Techniques Used to Assess Muscle Origin and Insertion:
- Palpation: Feeling the muscle with the hands to determine its origin and insertion.
- Imaging modalities: X-rays, MRI, and ultrasound can provide detailed images of muscles and their attachments.
- Physical examination: Testing muscle strength, range of motion, and palpation can help assess muscle origin and insertion.
Question Bank: Muscle Origin And Insertion Quiz
What is the difference between muscle origin and insertion?
Muscle origin refers to the fixed or less movable attachment of a muscle, while muscle insertion denotes the movable or more movable attachment.
How do muscle origin and insertion influence muscle function?
Muscle origin and insertion determine the direction of muscle pull, which in turn influences joint movement and overall muscle function.
Why is understanding muscle origin and insertion important in clinical settings?
Knowledge of muscle origin and insertion aids in diagnosing and treating musculoskeletal disorders by identifying muscle imbalances, injuries, and movement dysfunctions.